Spring NTEA CV Report shows industry return to 'normalcy,' demand down
The fourth edition of the semi-annual NTEA U.S. Commercial Vehicle Market Report found that 2023 was generally a growth and recovery year. This was driven by the industry naturally returning to pre-pandemic levels, as well as interst in fleets' interst in more sustainable vehicle options.
“Fueled by a resurgence of rental and leasing industry registrations along with fleets continuing to adopt alternative fuel vehicles, 2023 was a year of positive growth for the commercial vehicle industry,” said Mark Hazel, associate director, commercial vehicle reporting, at S&P Global Mobility.
Overall, the free report provided by Commercial Truck Trader, NTEA and S&P Global Mobility covered topics ranging from chassis shortages to inventory age and electric commercial vehicle (EV) trends. The report compares sales, registrations,a nd purchase consideration to provide dealers and industry stakeholders with historical data to help plan ahead and track trends.
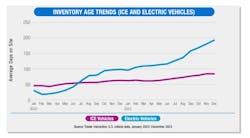
One of those trends is inventory age. Incomplete vehicles averaged just over 120 days on-site, while completed vehicle inventory age climbed from roughly 50 days to nearly 90.
However, stable inventory age wasn’t positive for all vehicles, as the report found EVs spent increased time on site. This is indicative of some problems the industry is having with transitioning to electric powertrains, a problem the report noted as EV registrations “continued to stall.” With inventory age climbing to almost 200 days, the use-case definition for EV targets will be important going forward.
But in contrast, the report also found that Class 2 EV registrations performed very well, particularly in November and December of 2023. Reportedly, November 2023 almost doubled registrations of November 2022.
Read more: New NTEA OEM guidance to ease upfitting
“Most vehicles available in the fourth quarter of 2023 in the commercial space were in the lighter Class 2a (pickup) and 2b (van) space,” the report explained. “Assuming continued growth in the availability of EV models, the result may be a greater spread in fuel and propulsion types.”
Industry working towards normalcy
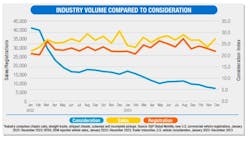
The report indicated that while not yet as strong as in 2019, the industry finished 2023 above 2021 and 2022 levels in terms of volume, “which indicates the market is still reacting to pent-up demand and on the way to returning to normal,” the report said.
That demand seems to be waning. While industry volume data showed sales were up from Jan. '22 to Dec. '23, the consideration index, which uses search data to measure potential purchaser effort to buy vehicles, dropped from about 35 down to just over 5.
For Class 8 chassis cab, though, monthly sales were up over 40% from Jan. '22 to Dec. '23, the Consideration Index dropped from nearly 60 to under 10 over the same period.
The Consideration Index tended to trend downward across several vehicle segments, including cutaway vans, cargo vans, Classes 2-5 chassis cabs, vocational vehicles, and cab over vehicles.
According to the report, decreasing consideration times indicated that vehicle availability is increasing, and that some fleets may be buying more vehicles straight off the lot and are able to find what they need, despite some shortages.
“Consideration continued to improve, pointing to a more normal market,” the report noted. “Sales and registrations flattened out as supply chain issues decreased and supply caught up to demand. Pent-up demand drove the market to some extent, especially in the higher weight classes.”
Supply and workforce shortages
Frame rail shortages continued to cause difficulties for the commercial vehicle market, as well as workforce shortages for much of the industry.
For frame rails, stripped chassis, Classes 3-5 chassis cabs, and commercial-use pickups had the most difficulties. In particular, the pickup segment experienced a decline in registrations in the second half of the year while strip chassis saw a large consideration decrease in Q3 due to a lack of this component.
Meanwhile, workforce shortages also impacted equipment manufacturers, distributors, and upfitters.
“Workforce shortages remained an issue for the majority of the industry, putting pressure on lead times, even when chassis were available, due to labor constraints related to vehicle upfitting,” NTEA’s report stated.
What to expect
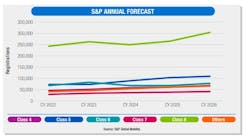
Going forward, S&P Global Market Intelligence generally raised its forecast of U.S. real gross domestic product growth for 2024 to 2.4%, while also lowering 2025’s forecast to 1.4%. While the Class 8 vehicle market has remained relatively strong with easing production constraints and high demand, the organization revised its forecast due to the “mixed effects of updated financial conditions on U.S. growth.” This is because S&P found equity valuations firmed up more and credit spreads were narrower than the company anticipated.
Additionally, a decrease in supply chain issues and ongoing fleet demand suggests that 2024 will be “the bottom of the current truck cycle, either flat or just incrementally above 2023,” S&P explained. This could lead to a 6.9% gain for medium-duty trucks, especially as Class 4 vehicles have benefitted from the growth of e-commerce. This Class 4 growth is likely to continue, S&P anticipated, as the market prepares for the more stringent 2027 emissions regulations, especially if diesel-truck buyers buy the last available pre-2027 vehicles throughout 2025-2026.
With all that said, the report found that fleets may have fewer customization choices going forward, as the industry may transition to technology updates instead of chassis updates. Especially with the upcoming emissions regulations, chassis OEMS will need to take advantage of updates to the proposed California Air Resources Board 2024 Heavy-Duty Engine and Vehicle Omnibus regulation for MY 2024-2026 vehicles.
What this means for fleets is that planning ahead for vehicle purchases is paramount. Not only must they keep in mind their allocations for vehicle purchases, but they should examine the pros and cons of ordering vehicles from dealerships versus the dealer stock.